Dr. Jitendra Mohan Agarwal (Ph.D. Chemistry), Chemistry Lecturer, G.I.C. Dineshpur (U.S. Nagar) UK.
Abstract: The present paper deals with the synthesis of Bromo Substituted and N-Substituted 4-biphenyl acetic acid amides by condensation of corresponding acid chlorides with suitable amines. The structure of newly synthesized compounds were elucidated on the basis of their IR, TLC, and elemental analysis data. The compounds were also screened for their anti-bacterial and anti-fungal activity.
Keywords: Synthesis, biphenyl derivatives, spectral and biocidal activity.
INTRODUCTION:
Biphenyls and polynculear aromtic hydrocarbons (PAHs) have been reported in the literature to found naturally at several places in the environment. American Chemical Society reported a novel palladium. catalyzed ullmann- type reductive coupling of aryl-halides, under an air atmosphere and in equeous acetone to obtain different type of biphenyl derivatives. (11-12) The newly synthesized Bromo Substituted and N-Substituted 4- biphenyl actamides derivatives are biocidal screening to evaluate their possible use as antifungal and antibacterial activities.
Experimental:
All the chemicals used for the synthesis were of Analar grade. Distill solvent were used throughout the experiment.
Procedure of Preparation of Fungus Solution:
Take distilled water (25 ml) in a conical flask and add some procelline pieces in it. Then, sterilized the conical flask in autoclave upto 100 mm. pressure, Now, the pressure of autoclave comes down upto zero Point, then release the Pressure of autoclave and wait for few minuts. Now, open the autoclave and Put the conical flask on the table for achieving room temperature. then, inject very few quantity of fungus used for the growth such as :- Fujeerium-Udum with the help of Anaculation needle in sterilized medium. Now, Shake very well the conical flask to spread out the spares of fungus in the water finely.
Procedure of Growing the Fungus:
Take two petric plates and paur 1 ml. solution of fungus (used for the identification of antifungal Properties of compound) in each Petric Plate, add Agar-Agar Media (15ml) in each Petric Plate. Then, wait for 4-5 days for the growth of fungus in these Petric Plates.
After the browth of particular fungus, cut the fungus of a particular size (3mm). These blocks were replaced in another petric plate alongwith Czapeck’s media (15ml) and the solution of compound (1ml). Now, the identification of antifungal property of a Particular compound on specific fungus might be Possible.
Synthesis of Compounds:
This paper includes the synthesis of simple Bromo Substituted and N-Substituted 4-biphenyl acetamides analoges. The syhthesis of Bromo Substituted 4-biphenyl acetamides containing three step. and the synthesis of N-Substituted 4-biphenyl acetamides containing two steps. In 1st step converted 4-biphenyl acetic acid(13) (4-BPAA) into 4-biphenyl acetyl chloride [4-BPAC (as a various liquid)] by refluxing 4-BPAA with thionyl chloride in dry benzene for 2 ½ hours and in 2nd step viscous oil treated with different type of suitable amines at room temp in the presence of 4N-NaOH by stirring, in order to prepared different types of amides of 4BPAA. This scheme is clear from following diagramatic representation.
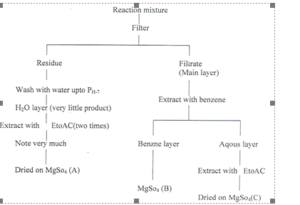
Ist Step 4 – BPAC (1gm) in dry benzene (25 ml) {benzene distilled over on anhydrous Cacl21 and thionyl chloride (1ml) added in a 100 ml of R.B. flask, and refluxed the reaction mixture for 2 ½ hrs. After 1 hour the colour of mixture change from yellow to brown. After 2 ½ hrs thionyl chloride along with benzene. Traces of thionyl chloride removed with the help of vaccum pump 4-Biphenyl acetyl chloride obtained in oily form and w3ecl without further purification in next step to form different types of amides of 4-BPAA.
IInd Step 4 – E3PAC (875 mg), benzene (25m1), ethyl acetate (25ml) and aqous ammonia (3.0 ml + 15 ml water) one by one slowly add in a 250 ml of R.B. flask slowly under stirrng at room temp and stirring continue for 3 hrs. Workup the reaction mixture with benzene + Ethylacetate after 20 hrs, after checked the TLC of reaction mixture. Reaction mixture takes in a saperatory funnel along with distilled water. Compound is in the benzene layer, wash out the benzene layer with water 3-4 times to remove the basic nature of the benzene layer.
When benzene layer becomes neutral, this layer was taken in a conical flask and add MgSo4 (to absorb the moisture of benzene layer), wait for 5-10 minutes. Filtered the solution in a R.B. flask and recovered the benzene from reaction mixture by distillation and traces of benzene with the help of vaccum pump. Concentrate residue was treated with hexane for complete precipitation. Light pale yellow coloured crystalline solid compound obtained, filter through whatman filtervpaper No. 42, wash the ppt. with hexane 2-3 times, dry and weigh.
3rd Step – 4: Preparation of 3, 3’-Dibromo-N-phenyl – 4 – biphenyl acetamide (12A) from 3, 3’-Dibromo-4-Biphenyl acetyl chloride (1B).
Dissolved Anilline (250mg) in benzene (10ml) in a R.B. flask and add 4N-NaOH in it. Take 1B (542 mg) and dissolved it in dry benzene (10ml), then pour it slowly drop wise under stirring in the R.B. flask. Stirring continue for 3 hours and workup the reaction mixture after 20 hours.
The same procedure were synthesized Bromo Substituted and N-Substituted 4-Biphenyl acetamide derivatives such as:
A1 – (3, 3’ Dibromo – N – Phenyl – 4 Biphenyl acetamide) – 12A
A2 – (3, 3’ Dibromo – N – Phenyl – 4 Biphenyl acetamide) – 17A
A3 – (3, 3’ Dibromo – N – P – Tolune – 4 – Biphenyl acetamide) – 19A
A4 – (3, 3’ Dibromo – N – a – Naphthyl– 4 Biphenyl acetamide) – 15A
A5 – (3, 3’ Dibromo – N – Phenyl – Thiomide – 4 Biphenyl acetamide) – 16A
A6 – (3, 3’ Dibromo – N – Benzyl – 4 Biphenyl acetamide) – 17A
The same procedure were synthesized N-Substituted 4-Biphenyl acetamide derivatives such as –
- N-Benzoyl – 4 – Biphenyl acetamide (22A)
- N-Acetyle – 4 – Biphenyl acetamide (23A)
- N-Phenyl acetyl – 4 – Biphenyl acetamide (24A)
- N-Cinnamyl – 4 – Biphenyl acetamide (25A)
- N-Salicyloyl – 4 – Biphenyl acetamide (26A)
RESULT AND DISCUSSION:
Various types of amides of 4-BPAA having two-Co groups and laving-CO-NH-CO type bonding During the synthesis of such type of the compounds first of all we do the acetylation of 4 -BPAA as discussed earlier then 4-Biphenyl acetyle chloride (4 – BPAC) react with different types of uitable aliphatic and aromatic amines having free–NH2 group to prepare a various type of amides of 4-BPAA. The characteristic JR bands (4000-200 cm-1) for the 4-BPAA, 4-BPAC and 4-BPAA derivatives compounds provide meaningful information regarding the bonding sites of the amides. The IR spectra show characteristic bands in the region 3243-3255 cm-1 with free >NH2(14) and the region 1630-1645 cm-1 showed >CO group.
Synthesis of N-Substituted 4-biphenyl acetamides derivatives.
In this scheme commercially available and synthesized amides were used those having free-NI-12 group. But the results were not poor and an average 30-90% yield of such type of the synthesized amides obtained and with very few failures.
The analytical results, melting point, color, yield and 1R bands of the compounds are presented in table 1.
Biocidal Activity:
Result can be Summerised of Bromo Substituted 4 Biphenyl Acetamides Derivatives
S. No. | Code | Experimental yield (100%) | Yield obtained (%) |
1. | 12A | 570mg | 270mg (43.36%) |
2 | 13A | 480 mg | 290mg (60.42%) |
3 | 14A | 585 mg | 470mg (80.34%) |
4 | 15A | 630 mg | 570mg (90.48%) |
5 | 16A | 640 mg | 500mg (78.12%) |
6 | 17A | 880 mg | 780gm (88.64%) |
The compounds were also screened for their antifungal activity of disc-plate method (15 against C.lunata Seven days old culture were used as test organism which were grown on dextrose-agar medium. The fungi were grown at R.T. 10 ± 30C and the average of three replications was recorded with control plate. The percentage inhibition (16) was calculated as (C-T) x 100/C where C-diameters of fungus colony in control plate and T-diameter of Fungus colony in test plate.
Result can be Summerised of N – Substituted – 4 Biphenyl Acetamides Derivatives
S. No. | Code | Experimental yield (100%) | Yield obtained (%) |
1. | 22A | 685 mg | 260mg (43.96%) |
2 | 23A | 550 mg | 270mg (49.09%) |
3 | 24A | 685 mg | 200mg (29.20%) |
4 | 25A | 740 mg | 345mg (46.22%) |
5 | 26A | 720 mg | 360mg (50%) |
All the compounds show positive results and resist the growth of a particular fungus. This has been observed from experimental observations, that as the concentration of the solution of a particular compound increased, the resistant power of a particular compound was also increased to resist the growth of a particular fungus.
REFERENCES:
- Environmental Protection Agency; Fed. Regist. 65 (248), 81373- 81381(2000).
- Cunliffe, Adrian M; williams, paul T; J. Anal. App!. Pyrolysis, 44(2), 131-152(1998).
- Venkatraman, sripathy; Li, Chao-j im; Org Left. 1(2) 1133-1135 (1998).
- Hishizawa, Susumu; yamada seiji; Japan Kokai Tokyo Koho JP; 10, 53-55, (1998).
- Kushwaha, B.S; Sengar A-K; Singh, Jaipal; Oriental J. Chem.; 22(2), 411-414 (2006)
- F. Kuvangh; Analytical microbiology. Acadame press. New York (1963).
- J. M. Vincent, Farmers. Bull; USDA, 159, 850(1947).
- Sengar, A.K; Kushwaha, B.S; Singh, J; J. Chem tracks, 7 (1 & 2). 47-50(2005).
- Sharma, shweta; sharma, C; Dangli, RR and Tallesara G.L; J. Ind. Council Chem.; 26(2), 139-145, (2009).
- Malik, Suman; ghosh, S. and Jam, Bharti; J. Ind. Council Chem. 27(2). 173-176 (2010).
